The size of a warehouse can significantly impact logistics efficiency and operational costs, making it an important decision for any business. In the U.S., the average warehouse size is approximately 17,000 square feet, but warehouse sizes vary widely based on industry and business needs. Small warehouses typically range from 10,000 to 25,000 square feet, ideal for businesses with limited storage requirements. Large warehouses can exceed 500,000 square feet, accommodating extensive inventory and advanced logistics operations.
This article explores warehouse size variations, their benefits, and key considerations to help you determine the right fit for your business.
Key Takeaways
- Warehouse size significantly impacts logistics efficiency and operational costs, necessitating careful evaluation of storage needs.
- Small warehouses are ideal for businesses with limited inventory requirements due to their lower operational costs and flexibility, whereas large warehouses accommodate high-volume needs with advanced technologies.
- Key factors influencing warehouse size decisions include inventory volume, product types, and future growth projections, emphasizing the importance of strategic planning.
Smarter Warehouse Management Starts Here
From receiving to shipping, SphereWMS gives you real-time visibility and control over every square foot. See how it works for your operation.
Schedule Your DemoUnderstanding Warehouse Size
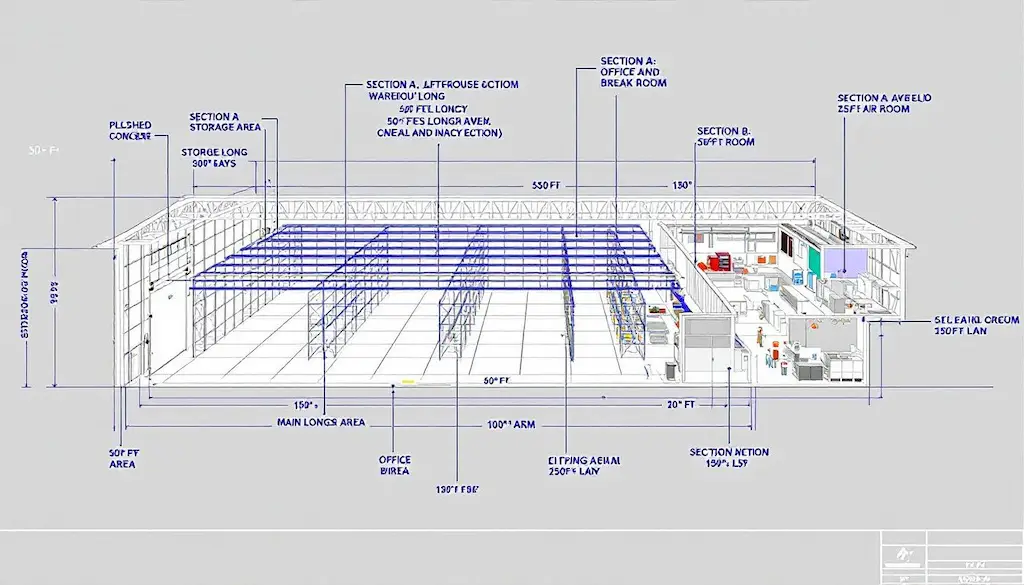
Warehouse size plays a pivotal role in logistics and supply chain management. The dimensions, layout, and specific needs of your shipping warehouse must be considered to ensure you have adequate storage capacity while maintaining operational efficiency.
Selecting the right warehouse size can greatly enhance storage efficiency and lower operational expenses.
What is the average warehouse size?
The average U.S. warehouse is approximately 17,000 square feet, though sizes vary significantly by business needs. Small warehouses range from 10,000-25,000 square feet for limited storage requirements. Large warehouses exceed 500,000 square feet for significant inventory volumes. Determine your needs by evaluating current inventory, growth projections, and product types—bulky items require considerably more space than compact goods.
Typical Warehouse Sizes by Industry
Warehouse size requirements vary significantly across industries, depending on storage needs, inventory turnover, and operational complexity. Here’s a look at typical warehouse sizes for different industries:
E-commerce & Retail: 50,000 – 300,000 sq. ft.
High SKU variety and fast inventory turnover require mid-to-large warehouses with efficient picking systems.Manufacturing & Industrial: 100,000 – 500,000+ sq. ft.
Facilities need space for raw materials, production, and storage, often including specialized zones for different stages of production.Food & Beverage: 10,000 – 200,000 sq. ft.
Cold storage and temperature-controlled warehouses tend to be smaller but require specialized infrastructure.Third-Party Logistics (3PL): 50,000 – 1,000,000+ sq. ft.
3PL providers manage multiple clients, requiring flexible space for varying storage and fulfillment needs.Pharmaceutical & Healthcare: 10,000 – 150,000 sq. ft.
Compliance-driven warehouses focus on controlled environments and security for regulated products.Automotive & Heavy Equipment: 100,000 – 1,000,000+ sq. ft.
Large warehouses store bulky parts, tools, and vehicles, requiring high ceilings and specialized handling equipment.
How to measure warehouse capacity
Warehouse capacity represents total available storage space including staging areas. Calculate usable capacity by subtracting non-storage areas like offices and aisles from total square footage. Consider height and overhead space while accounting for safety regulations on stacking. Warehouse capacity calculators help determine total usable volume. Accurate assessment ensures efficient storage solutions that comply with industry standards.
Small Warehouses: Benefits and Considerations
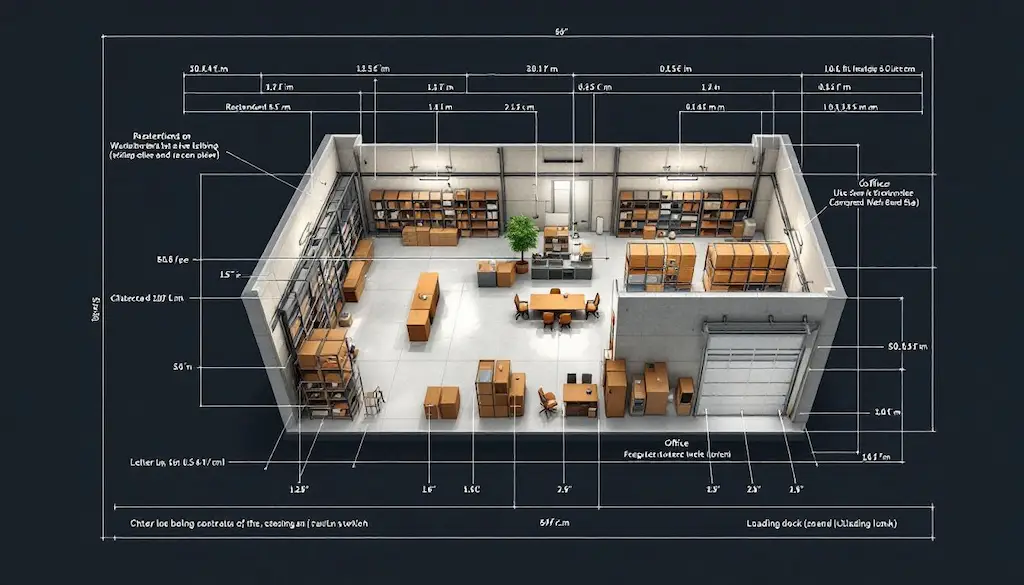
Small warehouses are an excellent option for businesses with limited storage needs or those looking to keep overhead costs low. These compact spaces are particularly beneficial for small businesses or startups that require efficient and cost-effective storage solutions, including small and large warehouses.
Knowing the traits, benefits, and challenges of small warehouses helps determine if they align with your business needs.
Characteristics of small warehouses
Small warehouses typically range from 5,000 to 15,000 square feet. These spaces are ideal for businesses with minimal inventory requirements or those that deal with products that have lower inventory turnover. Small warehouses often serve as specialized storage solutions, catering to specific storage needs without the high costs associated with larger facilities.
These warehouses are also beneficial for businesses that require quick and easy access to their inventory. The compact size allows for efficient organization and faster retrieval of goods, which is crucial for maintaining smooth operations. Additionally, small warehouses and shipping warehouses can be used as distribution centers for local deliveries, ensuring timely and cost-effective shipping.
Advantages of small warehouses
One of the primary advantages of small warehouses is their affordability. Lower operational and storage costs make these warehouses a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to minimize expenses. Small warehouses also offer operational efficiency due to their compact size, making inventory management simpler and more streamlined.
Flexibility is another significant benefit of small warehouses. These spaces allow businesses to scale their operations as needed without making substantial changes to their infrastructure. Lower inventory levels can reduce transportation costs and enhance cash flow management. Small warehouses enable businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions, enhancing their overall agility.
Challenges with small warehouses
Despite their benefits, small warehouses come with their own set of challenges. Limited storage space can lead to congestion and inefficiency, making it difficult to store diverse inventory types. As businesses grow and their inventory needs increase, small warehouses may struggle with scalability, potentially hindering business growth.
Moreover, small warehouses often lack advanced technological features that larger facilities possess. This can impact inventory tracking and management, leading to inefficiencies in operations. Businesses must carefully consider these challenges when evaluating whether a small warehouse is the right fit for their needs.
Large Warehouses: Benefits and Considerations

Large warehouses are designed to accommodate significant inventory volumes and complex operations. These expansive warehousing spaces are ideal for businesses with high-volume storage needs, offering extensive storage capacity and advanced technological capabilities, including larger warehouses.
Identifying the features, benefits, and challenges of large warehouses aids in deciding if they suit your business needs.
Characteristics of large warehouses
Large warehouses typically exceed 100,000 square feet in size, with some facilities spanning over 500,000 square feet. These warehouses are designed to accommodate substantial stock, making them suitable for businesses with high-volume operations. The layout of large warehouses often includes open spaces to facilitate the efficient movement of goods and the storage of bulky items.
The design of large warehouses also incorporates advanced technological features to streamline operations and improve efficiency. These features can include automated storage and retrieval systems, sophisticated inventory management systems, and advanced material handling equipment. Utilizing these technologies can boost operational efficiency and lower labor costs.
Advantages of large warehouses
One of the primary advantages of large warehouses is their ability to integrate advanced technologies. These technologies can significantly streamline operations, improving inventory accuracy and enhancing retrieval efficiency. Large warehouses also offer the benefit of bulk pricing, allowing businesses to purchase inventory in larger quantities at reduced costs.
Moreover, large warehouses provide extensive storage capacity, accommodating a wide range of products and higher inventory volumes. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that experience seasonal fluctuations or have diverse product lines. With ample storage space, large warehouses allow effective inventory management and can meet rising demand without extra costs.
Challenges with large warehouses
While large warehouses offer numerous advantages, they also come with significant challenges. Higher operational costs are a primary concern, as large warehouses require more resources for utilities, maintenance, and labor. Additionally, managing large warehouses introduces complexity, particularly in maintaining inventory accuracy and ensuring efficient workflows.
Businesses must also consider the potential for bottlenecks and inefficiencies in large warehouse operations. Effective inventory control, picking and packing processes, and streamlined workflows are essential to prevent operational disruptions. Tackling these challenges ensures large warehouses run smoothly and efficiently.
Key Factors Influencing Warehouse Size
Several key factors influence the choice of warehouse size, including inventory volume, product types, business growth projections, and operational efficiency. Grasping these factors is crucial for choosing a warehouse size that matches your business needs and growth plans.
Inventory volume and product types
The amount of inventory you plan to store and the types of products you handle are critical factors in determining the appropriate warehouse size. Large warehouses are suitable for significant inventory volumes, accommodating substantial stock without incurring excess costs. However, having too much inventory can lead to increased costs, wasted space, and unsellable products, necessitating efficient warehouse management.
Insufficient inventory can result in stockouts and backorders, impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Businesses must consider factors such as customer demand, SKU usage, seasonality, and shifting trends when evaluating their storage needs. Evaluating these elements helps companies choose the optimal warehouse size for adequate storage and efficient operations.
Business growth projections
Planning for future growth is essential when choosing a warehouse size. Underestimating future storage needs can lead to costly relocations and disruptions in operations. Planning for future expansion ensures businesses have ample space for rising demand, avoiding frequent relocations.
Operational efficiency and workflow
Operational efficiency and workflow are crucial factors in warehouse size planning. Understanding warehouse workflow can uncover effective methods to improve space usage and streamline operations. The location and size of packing areas should be aligned with shipping zones to enhance efficiency and reduce bottlenecks.
Managing large warehouses can introduce complexities, particularly in maintaining inventory accuracy and ensuring efficient workflows. Utilizing advanced systems and technologies can help businesses manage higher inventory volumes and improve operational efficiency.
Optimizing warehouse layout and workflows maximizes storage space and boosts overall productivity.
Maximizing Warehouse Storage Space
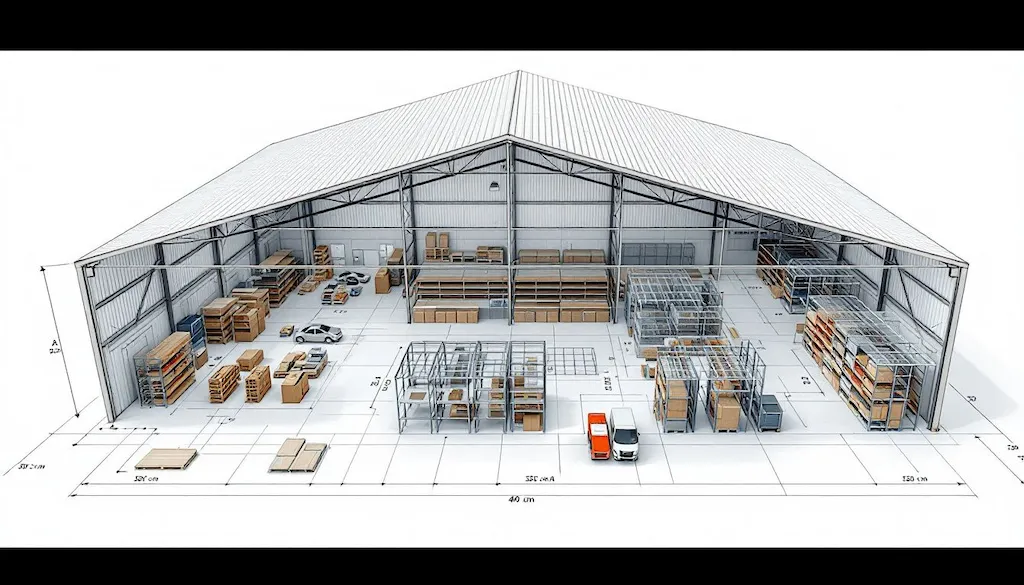
Maximizing warehouse storage space is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and enhancing storage capacity. Effective storage methods, warehouse management systems, and optimized layouts help businesses maximize space and improve operations.
Effective storage methods
Effective storage methods are crucial for maximizing warehouse space. Utilizing vertical space, such as extending racking systems, can significantly enhance storage capacity. Reducing aisle widths can free up 15 to 20 percent of the total storage area, providing more space for inventory.
Mobile pallet racking systems are another effective storage solution, allowing aisles to open and close automatically to maximize storage without sacrificing access. Block stacking, while cost-effective, can limit accessibility and should be used strategically to optimize space.
These storage methods maximize warehouse efficiency and storage capabilities.
Utilizing warehouse management systems
Warehouse management systems (WMS) are essential tools for optimizing warehouse space and improving operational efficiency. These systems can direct inventory placement, suggesting the best locations for specific pallets based on inventory turnover. Using a WMS enhances inventory management and maximizes space utilization.
WMS also play a crucial role in real-time inventory tracking, ensuring that businesses have accurate and up-to-date information on their stock levels. This helps in optimizing product locations and improving retrieval efficiency, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of warehouse operations.
Optimizing warehouse layout
An optimized warehouse layout is essential for maximizing storage space and ensuring smooth operations. Effective layout planning involves considering racking capabilities, SKU characteristics, and the proximity of top-sellers to packing stations. By strategically placing high-turnover items near packing areas, businesses can streamline their picking processes and reduce travel time within the warehouse.
Additionally, optimizing warehouse layout requires addressing factors such as aisle width, storage density, and the configuration of pallet racks. Utilizing space-saving techniques like vertical storage and mobile racking systems can help businesses maximize their available space and improve overall efficiency.
A well-planned layout enhances storage capabilities and ensures smooth warehouse operations.
Choosing the Right Warehouse Size for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate size for a warehouse is crucial. It significantly influences the effectiveness of your business operations. Companies should evaluate their current storage needs and anticipate future growth to select the appropriate warehouse size.
Considering inventory volume, operational efficiency, and growth projections helps ensure adequate storage space for operations.
Assessing current and future needs
Assessing both current and future storage needs is the first step in selecting the right warehouse size. It is necessary to have enough room for total inventory plus safety stock to meet immediate warehouse storage needs.
Forecasting future growth and peak season needs can help businesses plan for additional storage space and avoid costly relocations to larger facilities.
Consulting with experts
Consulting with warehouse design experts can provide valuable insights into selecting the optimal warehouse size for your business. Experts can assess your storage needs, operational requirements, and future growth projections to determine the appropriate size and layout for your warehouse.
If facing a capacity issue, outsourcing to an expert can help with warehouse storage expansion and ensure that your storage solutions are both efficient and scalable.
Summary
In conclusion, selecting the right warehouse size involves careful consideration of various factors, including inventory volume, product types, business growth projections, and operational efficiency. Both small and large warehouses offer unique benefits and challenges that businesses must evaluate to determine the best fit for their needs. By maximizing warehouse storage space through effective storage methods, utilizing warehouse management systems, and optimizing warehouse layout, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and support their growth. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, choosing the right warehouse size is crucial for ensuring the success of your operations and achieving your long-term objectives.
Choosing the right warehouse size is just the beginning—optimizing your operations is what truly drives efficiency. Sphere WMS helps businesses streamline inventory management, improve order accuracy, and maximize warehouse space. Contact us today to see how Sphere WMS can support your warehousing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average size of a medium warehouse?
The average size of a medium warehouse ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 square feet. This size strikes a balance between efficient storage and operational productivity.
What is the standard small warehouse size?
The standard small warehouse size typically ranges from 5,000 to 15,000 square feet. This size is well-suited for businesses with limited storage needs.
How big is a 5000 square foot warehouse?
A 5,000 square foot warehouse measures approximately 50 feet by 100 feet. This size offers ample space for storage and operations, making it a functional and flexible solution for various needs.
What is the average size of a warehouse?
The average size of a warehouse varies significantly, with typical sizes around 17,500 square feet or approximately 180,000 square feet in the U.S., depending on the industry and business needs. Therefore, businesses have a wide range of options to choose from.
What is the average warehouse size in the U.S.?
The average warehouse size in the U.S. is approximately 17,000 square feet, although this can vary based on individual business requirements.




