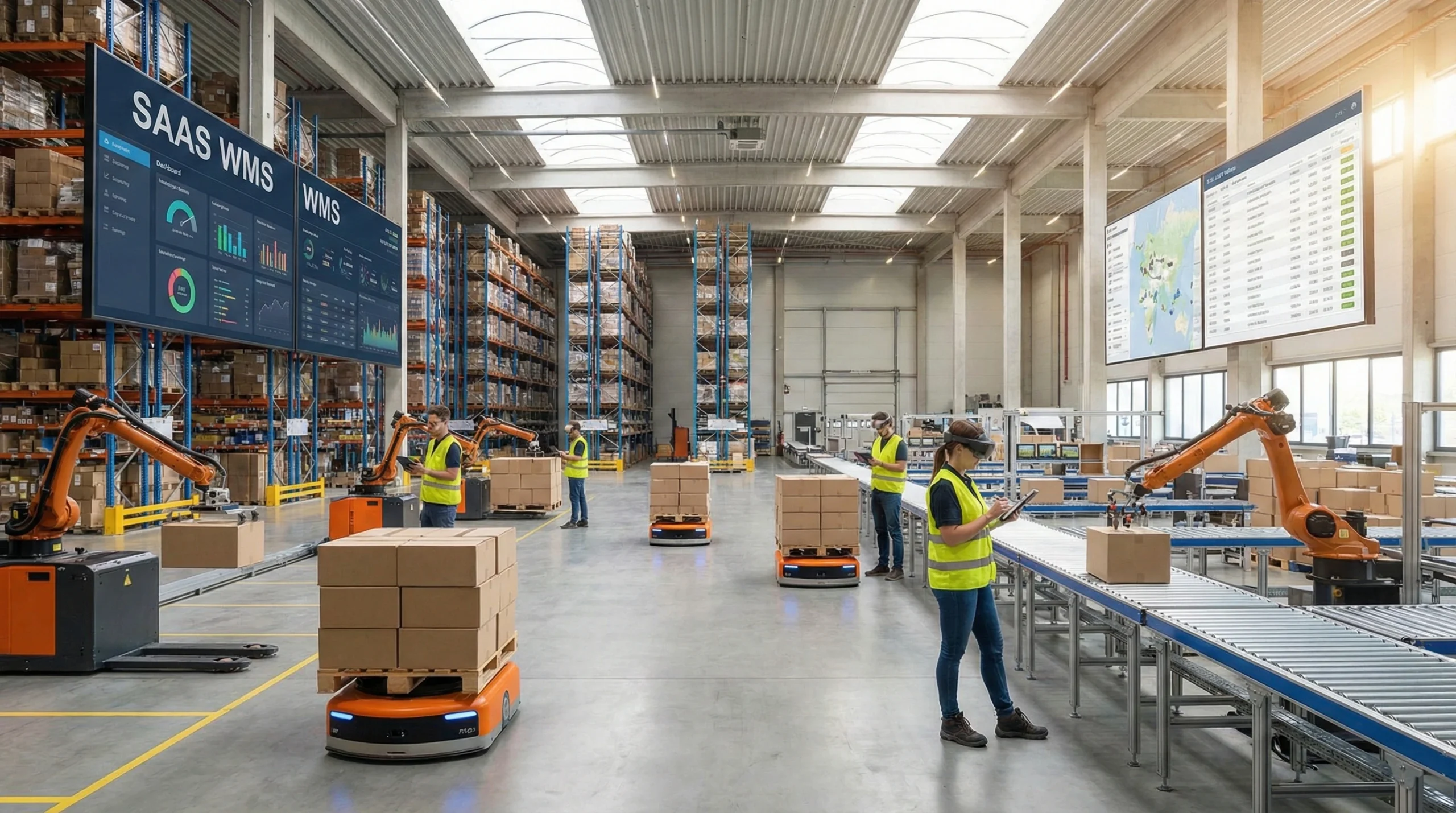
Enhanced Scalability and Flexibility
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, warehouse operations face constant fluctuations in demand, seasonal peaks, and unexpected market shifts that can strain traditional warehouse management systems. Cloud-based Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions offer unparalleled scalability that traditional on-premises systems simply cannot match. This adaptability allows businesses to efficiently adjust their warehouse operations without the significant hardware investments or system overhauls that were once necessary. The elastic nature of cloud infrastructure means companies can scale their computing resources up during high-volume periods such as holiday seasons and scale down during quieter periods, effectively matching operational costs to actual business needs rather than maintaining capacity for peak scenarios year-round.
Many growing businesses particularly benefit from this flexibility, as evidenced by mid-sized retailer Atlantic Supply, which expanded from managing 5,000 SKUs to over 15,000 in just 18 months without any significant disruption to their operations or additional IT infrastructure investments. Their cloud-based WMS automatically allocated additional resources during this growth period, maintaining system performance while transaction volumes tripled. The scalability extends beyond just handling more inventory or transactions—it also applies to user accounts, warehouse locations, and integration capabilities. When Atlantic Supply opened two additional distribution centers, they simply extended their existing cloud WMS pricing to the new facilities, achieving operational consistency across all locations while avoiding the complexity of managing multiple systems or undergoing extensive reconfiguration.
The flexibility of cloud-based systems extends to mobile accessibility, allowing warehouse managers and executives to monitor operations, make decisions, and adjust strategies from anywhere with an internet connection. This mobility has proven invaluable for businesses with multiple locations or those requiring management oversight across different geographic regions. During unexpected disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with cloud-based WMS were able to implement remote management practices more efficiently, maintaining operational continuity while ensuring staff safety. The subscription-based model of SaaS solutions further enhances flexibility by allowing businesses to adjust their service levels based on current needs without being locked into rigid licensing agreements or hardware configurations.
For seasonal businesses, this scalability presents a particularly compelling advantage. Consider Alpine Outdoor Equipment, which experiences 70% of its annual sales volume during winter months. With their cloud-based WMS, they easily scale up processing capacity during peak season without maintaining excess capacity year-round. This dynamic scaling allowed them to reduce their overall IT costs by approximately 30% while improving order fulfillment rates during their busiest periods. The ability to adapt quickly to changing business conditions without significant capital investment represents one of the most valuable aspects of cloud-based WMS solutions in today’s uncertain and rapidly evolving business environment.
Smarter Warehouse Management Starts Here
From receiving to shipping, SphereWMS gives you real-time visibility and control over every square foot. See how it works for your operation.
Schedule Your DemoCost-Effectiveness and Reduced Capital Expenditure
The financial advantages of implementing cloud-based WMS and SaaS solutions extend far beyond simple cost savings, representing a fundamental shift in how warehouse technology investments are structured and managed. Traditional on-premises WMS implementations typically require substantial upfront capital expenditure—including server hardware, networking equipment, database licenses, and the physical infrastructure to house these components—often amounting to hundreds of thousands of dollars before the system processes a single order. In contrast, cloud-based solutions convert these large capital expenditures into predictable operational expenses through subscription-based pricing models, allowing companies to preserve capital for other strategic investments while still accessing enterprise-grade warehouse management capabilities. This subscription approach typically includes maintenance, security updates, and technical support, eliminating many hidden costs associated with traditional systems.
The total cost of ownership (TCO) difference becomes increasingly apparent when considering the ongoing expenses of traditional systems. On-premises solutions require dedicated IT staff for maintenance, regular hardware refreshes every 3-5 years, cooling systems, power backup solutions, and physical security measures—costs that are largely absorbed by the service provider in cloud deployments. Industry analysis indicates that over a five-year period, the TCO for cloud-based WMS solutions can be 25-50% lower than comparable on-premises deployments, with the differential becoming more pronounced for smaller and medium-sized businesses that lack economies of scale in IT operations. Pharmaceutical distributor MedSupply Direct, for example, calculated a 42% reduction in five-year technology costs after migrating from their legacy on-premises system to a cloud-based WMS, while simultaneously increasing their operational capabilities and eliminating the need to hire additional IT personnel.
The economic benefits extend to implementation timelines as well, with cloud-based systems typically deployed in 50-70% less time than traditional solutions. This accelerated implementation translates directly to faster return on investment and reduced disruption to warehouse operations during the transition period. Companies can often begin realizing productivity improvements within weeks rather than months, creating a compounding economic advantage. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go model enables businesses to align their technology expenses more closely with actual usage and business results, creating a more direct connection between costs and value that was previously difficult to achieve with fixed-cost systems.
Perhaps most significantly, cloud-based solutions reduce financial risk by eliminating the possibility of expensive implementation failures that have historically plagued on-premises WMS deployments. The modular nature of SaaS WMS allows companies to start with core functionalities and expand as needed, preventing the “all-or-nothing” risk profile of traditional implementations. Fashion retailer StyleCo initially deployed only basic inventory and order management modules of their cloud WMS overview, adding advanced features like wave planning and labor management only after establishing baseline operations and validating system performance. This phased approach reduced their financial exposure while still allowing them to achieve a comprehensive solution, demonstrating how cloud-based systems can fundamentally transform the risk-reward equation of warehouse technology investments.
Improved Data Accessibility and Real-Time Updates
The transformation of warehouse data from historical records to actionable real-time intelligence represents one of the most powerful advantages of cloud-based WMS solutions in today’s fast-paced logistics environment. Traditional warehouse systems often operated with significant data latency, where information about inventory levels, order status, and operational metrics might be updated only periodically—sometimes with delays of hours or even overnight batch processing. Cloud-based WMS platforms eliminate these delays through continuous data synchronization and real-time processing capabilities, enabling managers to access current operational status from any location at any time. This immediate visibility empowers decision-makers to respond proactively to developing situations rather than reacting to problems that may have begun hours earlier, fundamentally changing the speed and agility with which warehouses can operate.
The accessibility benefits extend well beyond the warehouse walls, creating seamless information flows throughout the entire supply chain ecosystem. Sales teams can check actual inventory availability while meeting with customers, executives can monitor KPIs from mobile devices while traveling, and external partners like carriers and suppliers can access relevant data through secure portals—all interacting with the same real-time information. Continental Electronics implemented a cloud-based WMS that provided their customer service representatives with instant visibility into order status and inventory positions, reducing “where is my order” calls by 64% and cutting average call handling time by over three minutes. The system also automatically notified customers about order progress, proactively addressing potential concerns and improving overall customer satisfaction scores by 28% within the first six months of implementation.
The real-time nature of cloud-based systems creates particularly valuable capabilities for multi-location operations, where synchronized inventory visibility across distribution centers enables more sophisticated fulfillment strategies. Companies can implement intelligent order routing to select the optimal fulfillment location based on proximity to customer, current workload, inventory availability, and other dynamic factors—capabilities that would be technically challenging and prohibitively expensive with traditional systems. Global hardware distributor FastenRight leverages this functionality to automatically balance workloads across their seven distribution centers, reducing shipping costs by 12% while improving delivery times by selecting the optimal fulfillment location for each order based on real-time operational conditions rather than static rules.

The democratization of data access through cloud-based platforms also facilitates more collaborative and informed decision-making throughout the organization. Warehouse associates equipped with mobile devices can access relevant information on the warehouse floor, supervisors can monitor team performance in real time, and management can receive automated alerts when key metrics fall outside acceptable ranges. This operational transparency drives accountability and continuous improvement by making performance visible at all levels. Automotive parts distributor PrecisionDrive credits this improved data accessibility with helping them identify and address productivity bottlenecks, resulting in a 22% improvement in units picked per labor hour within their first year of cloud WMS inventory tracking implementation—improvements that would have been difficult to achieve without the immediate feedback loops that real-time data provides.
Easier Integration with Other Software
The ability to seamlessly connect warehouse operations with other business systems represents a defining characteristic of modern cloud-based WMS solutions, breaking down the data silos that have historically hampered efficiency and visibility across supply chains. Traditional on-premises warehouse systems often operated as islands of automation, requiring complex, custom-built interfaces to communicate with other enterprise applications like ERP systems, transportation management software, e-commerce platforms, and customer relationship management tools. Cloud-based WMS solutions fundamentally change this paradigm through standardized API (Application Programming Interface) architectures, pre-built connectors for common business applications, and interoperability designed as a core feature rather than an afterthought. This architectural approach dramatically reduces integration complexity, allowing businesses to create unified information flows that span the entire order-to-cash cycle.
The integration capabilities of cloud WMS extend far beyond simple data exchange, enabling sophisticated process orchestration across multiple systems. For example, when an order is placed through an e-commerce platform, the information can automatically flow to the cloud WMS, which then coordinates with inventory management to allocate stock, generates picking tasks, communicates with transportation management systems to select optimal shipping methods, updates the customer record in the CRM with tracking information, and sends the invoice details to the accounting system—all without manual intervention. Home furnishings retailer ComfortDwell implemented such an integrated ecosystem, reducing order processing time by 76% while decreasing data entry errors by 94%, demonstrating how proper system integration directly impacts both operational efficiency and customer experience.
The integration advantages become particularly valuable when connecting to emerging technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) devices, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and advanced analytics platforms. Cloud-based WMS solutions can ingest data from warehouse sensors monitoring environmental conditions, connect with automated picking robots to coordinate workflows, and feed operational data to artificial intelligence systems that identify optimization opportunities. Distribution company ElectroSupply leveraged these capabilities to create a hybrid workforce where their cloud WMS orchestrates tasks between human pickers and autonomous robots, dynamically assigning work based on order characteristics and current warehouse conditions. This integration increased their throughput capacity by 43% while maintaining the same physical footprint and staffing levels.
Perhaps most importantly, cloud-based integration significantly reduces the time and cost associated with connecting new technologies and business partners. The addition of a new sales channel, supplier portal, or logistics partner that might have previously required months of custom development work can often be accomplished in days through standardized integration approaches. This rapid integration capability enables businesses to be more responsive to market opportunities and operational challenges. When industrial supplier BearingSource needed to quickly establish drop-shipping capabilities with twenty new suppliers during supply chain disruptions, their cloud WMS allowed them to onboard these partners in less than three weeks—a process that would have taken months with their previous on-premises system. This integration agility has become a critical competitive advantage in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.

Enhanced Security and Reliability
The security and reliability of warehouse management systems have evolved from IT concerns into strategic business imperatives as supply chains become increasingly digitized and interconnected. Cloud-based WMS solutions offered by reputable providers typically deliver security capabilities that far exceed what most individual companies could implement independently, leveraging economies of scale to deploy sophisticated protection measures across their entire customer base. These comprehensive security frameworks include multiple layers of defense: physical security at data centers with controlled access and environmental monitoring; network security through advanced firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular penetration testing; application security with secure coding practices and vulnerability scanning; and data security through encryption both in transit and at rest. Leading cloud WMS providers maintain dedicated security teams that continuously monitor for emerging threats and apply patches immediately—a stark contrast to the often delayed update cycles of on-premises systems.
The reliability advantages of cloud-based systems stem from their architectural foundations, which typically include redundant infrastructure designed to eliminate single points of failure. Enterprise-grade cloud WMS solutions maintain distributed server architectures across multiple geographic regions, automated failover capabilities, and real-time data replication that ensures continuity even if an entire data center experiences an outage. These reliability features translate directly to business continuity, with leading cloud WMS providers offering service level agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing 99.9% or greater uptime—equating to less than 9 hours of downtime per year. Medical supply distributor HealthFlow credits their cloud WMS reliability for maintaining continuous operations during a regional power outage that affected their physical warehouse; while they operated on backup generator power for local equipment, their WMS remained fully functional through the cloud, allowing them to continue fulfilling critical medical orders without system interruptions.
The security and compliance advantages become particularly valuable for companies operating in regulated industries or handling sensitive data. Cloud WMS providers specializing in these sectors maintain comprehensive compliance programs aligned with industry standards like HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for payment processing, and various international data protection regulations. This built-in compliance significantly reduces the regulatory burden on individual companies, as the cloud provider assumes responsibility for maintaining appropriate controls and regularly validating them through independent audits and certifications. Pharmaceutical distributor MedCorpSupply leveraged these capabilities to expand into new international markets, relying on their cloud WMS provider’s regional data centers and compliance expertise to navigate complex data sovereignty requirements across multiple jurisdictions without having to develop this specialized knowledge internally.
The disaster recovery capabilities inherent in cloud-based systems represent perhaps their most compelling reliability advantage. Traditional on-premises WMS implementations often required complex, expensive, and infrequently tested disaster recovery plans involving backup sites and manual recovery procedures. Cloud-based solutions transform this approach through automated, continuously verified backup processes, geographically distributed data storage, and the ability to rapidly restore operations in alternative locations if needed. When manufacturing supplier IndustrialEdge experienced a warehouse fire that destroyed their on-site servers, they were able to resume operations from a temporary location within 24 hours because their cloud-based WMS remained intact and accessible—demonstrating how cloud solutions can fundamentally change the disaster recovery equation from a question of if operations can be restored to simply how quickly they can be resumed.
Automatic Updates and Upgrades
The continuous evolution of warehouse management technology has traditionally presented a significant challenge for businesses relying on on-premises systems, often leaving them struggling with outdated software or facing disruptive, expensive upgrade projects every few years. Cloud-based WMS solutions fundamentally transform this dynamic through their automated update and upgrade processes, ensuring customers always have access to the latest features, security patches, and performance improvements without the disruption and expense associated with traditional upgrade cycles. These updates typically occur in the background, often during planned maintenance windows, with minimal or no impact on daily operations. The frequency of these updates—sometimes delivered monthly or quarterly rather than every few years—creates a continuous improvement cycle that helps warehouses maintain technological currency and competitive advantage without requiring dedicated IT projects or additional capital investment.
The automatic update model delivers particular value through its ability to rapidly deploy new capabilities in response to emerging business requirements or market conditions. When the COVID-19 pandemic suddenly changed operating requirements for many warehouses, cloud WMS providers were able to quickly develop and deploy new features supporting contactless operations, social distancing workflows, and remote management capabilities—delivering these enhancements to all customers simultaneously through their standard update process. Electronics distributor CircuitPro benefited from this agility when their cloud WMS provider introduced advanced wave planning algorithms that improved their order batching efficiency by 28%, functionality they accessed immediately without additional cost or implementation effort simply because it was included in a regular platform update.
The upgrade process for cloud-based systems also eliminates many traditional risks associated with major version changes in warehouse software. Historical on-premises upgrades often required extensive testing, custom code migration, and weekend “cutover” events that created significant operational risk and business disruption. Cloud WMS providers mitigate these risks through architectural approaches that maintain compatibility across versions, automated testing of all customer configurations against new releases, and phased deployment strategies that allow for immediate rollback if issues arise. This risk reduction enabled food distributor FreshSource to benefit from three major feature upgrades to their cloud WMS within a two-year period without experiencing any significant operational disruptions—a pace of innovation that would have been practically impossible with traditional systems.
Perhaps most significantly, the automatic update model democratizes access to innovation across businesses of all sizes. Historically, smaller companies often struggled to keep pace with warehouse technology advancements due to limited IT resources and the high costs associated with upgrades. Cloud-based solutions level this playing field by delivering the same cutting-edge capabilities to all customers regardless of size, creating a more competitive marketplace where companies differentiate through how effectively they leverage technology rather than simply by who can afford the latest version. Regional distributor ValleySupply, with just two warehouses and 45 employees, now operates with the same advanced inventory optimization algorithms and machine learning-powered demand forecasting as their largest competitors—capabilities that would have been financially out of reach in the traditional on-premises software model but are automatically included in their cloud WMS subscription.
Support and Training from Providers
The relationship between businesses and their WMS providers has evolved dramatically with the shift to cloud-based solutions, transforming from transactional software purchases to ongoing strategic partnerships focused on mutual success. This evolution is particularly evident in the comprehensive support structures that accompany most cloud-based WMS deployments. Unlike traditional models where support might be limited to technical troubleshooting or available only through expensive maintenance contracts, cloud WMS providers typically offer multi-tiered support services included within their subscription fees. These support ecosystems often include 24/7 technical assistance through multiple channels, dedicated customer success teams that proactively monitor system health and usage patterns, and regular business reviews to ensure the solution continues to meet evolving needs. The continuous nature of the subscription relationship fundamentally aligns incentives between providers and customers, as vendors must regularly demonstrate value to earn continued business rather than focusing primarily on initial sales.
The training advantages of cloud-based solutions stem from both their delivery methods and continuous improvement cycles. Modern cloud WMS platforms typically incorporate embedded learning tools like contextual help, interactive tutorials, and simulation environments that allow users to practice procedures in a risk-free setting before performing them in production. These capabilities create more effective onboarding experiences and reduce the learning curve for new employees. Industrial parts distributor MechSupply leveraged these tools to reduce new hire training time by 62% while simultaneously improving task accuracy rates, allowing them to more effectively manage seasonal staffing fluctuations. Additionally, the regular update cycles of cloud solutions create natural opportunities for incremental training on new features, replacing the massive retraining efforts often required with major version upgrades of traditional systems.
The provider relationship extends beyond just software support to include access to specialized expertise and industry best practices that can help optimize warehouse operations. Leading cloud WMS providers employ specialists with deep domain knowledge in various aspects of warehouse management—from slotting optimization and labor management to inventory control and quality processes. These experts often work directly with customers to apply their knowledge to specific operational challenges, functioning almost as extensions of the internal team. When third-party logistics provider GlobalFreight wanted to improve their cross-docking efficiency, their cloud WMS provider conducted a focused optimization workshop that included both system configuration changes and procedural improvements, resulting in a 34% reduction in cross-dock cycle time and significantly improved dock utilization.
The community aspects of cloud-based solutions provide another valuable dimension to the support ecosystem. Many cloud WMS providers facilitate knowledge sharing among their customer base through user communities, annual conferences, specialized training events, and shared best practice repositories. These collaborative environments allow businesses to learn from others facing similar challenges and expand their knowledge beyond what internal resources alone might develop. Regional distributor WestCoast Supply credits their participation in their cloud WMS provider’s user community with helping them identify and implement voice-directed picking processes that increased productivity by 23%—an innovation they discovered through a case study presentation from another customer in a different industry who had successfully implemented the technology. This network effect of shared knowledge and collective experience represents a significant advantage over the often isolated nature of traditional on-premises implementations.
Conclusion
The transformation of warehouse management through cloud-based WMS and SaaS solutions represents far more than a simple technological shift—it fundamentally changes how businesses approach operational agility, financial planning, and continuous improvement in their supply chain operations. The seven benefits explored in this article—enhanced scalability, cost-effectiveness, improved data accessibility, easier integration, enhanced security, automatic updates, and comprehensive support—combine to create a compelling case for cloud adoption across businesses of all sizes. As supply chains continue to face unprecedented challenges from disruption, demand volatility, and labor constraints, the flexibility and resilience provided by cloud-based solutions become increasingly valuable strategic assets rather than merely IT considerations.
The shift toward cloud-based warehouse management aligns perfectly with broader business trends toward digital transformation, data-driven decision making, and operational agility. Organizations that embrace these technologies position themselves to respond more effectively to changing market conditions, scale operations efficiently to meet demand fluctuations, and continuously incorporate innovations without disruptive upgrade cycles. Perhaps most importantly, cloud-based WMS solutions free logistics professionals from many of the technical burdens of system maintenance, allowing them to focus their expertise on strategic improvements and customer service rather than IT management. As you consider your warehouse technology strategy, evaluate how these seven benefits might transform your specific operations and create competitive advantages in your market segment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between SaaS and Cloud-Based WMS?
While closely related, these terms have distinct meanings in the warehouse technology landscape. SaaS (Software as a Service) refers to a software delivery model where applications are licensed on a subscription basis and centrally hosted by the provider, eliminating the need for customers to install and maintain hardware or software. Cloud-Based WMS is a broader category that encompasses any warehouse management system deployed on cloud infrastructure, which may include different service models such as SaaS, Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). All SaaS WMS solutions are cloud-based, but not all cloud-based WMS solutions follow the SaaS model—some may require dedicated cloud instances or customer-managed components while still leveraging cloud infrastructure.
How does a cloud-based WMS improve warehouse efficiency?
Cloud-based WMS solutions drive efficiency improvements through multiple mechanisms: they provide real-time visibility across operations, enabling faster decision-making and issue resolution; they optimize workflows through intelligent task assignment and routing; they reduce manual data entry through automated data capture technologies like barcode scanning and IoT integration; they improve inventory accuracy through perpetual counting and location management; they enhance labor productivity through performance monitoring and incentive programs; and they reduce fulfillment errors through systematic verification processes. These capabilities collectively minimize wasted movement, reduce processing times, optimize resource allocation, and improve accuracy—all contributing to overall warehouse efficiency. Additionally, the continuous improvement model of cloud solutions means efficiency enhancements are regularly added through software updates without requiring major system changes.
Are there any risks associated with migrating to a cloud-based WMS?
While cloud-based WMS offers significant advantages, several risks should be carefully managed during migration: potential internet connectivity issues that could impact system access; data security and privacy concerns, particularly for sensitive information; dependency on the provider’s infrastructure and support capabilities; possible integration challenges with legacy systems; and the organizational change management required to adapt processes and staff to new workflows. However, these risks can be effectively mitigated through proper planning: implementing redundant internet connections, thoroughly vetting provider security practices and certifications, establishing clear service level agreements, conducting comprehensive integration testing, and developing robust change management programs with adequate training. When properly managed, the benefits of cloud-based WMS typically far outweigh these potential risks.
Can small to medium-sized enterprises benefit from cloud-based WMS?
Small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often realize even greater proportional benefits from cloud-based WMS than larger organizations due to several factors: the subscription model eliminates prohibitive upfront investments that previously made advanced WMS capabilities inaccessible to smaller operations; the reduced IT support requirements are particularly valuable for organizations without dedicated IT departments; the scalability allows systems to grow alongside the business without requiring periodic replacements; and the continuous updates provide access to the same advanced features used by larger competitors without additional investment. Many cloud WMS providers offer tiered solutions specifically designed for SMEs, with streamlined implementation processes and core functionality focused on the most critical warehouse operations, creating accessible entry points that can expand as the business grows.
How does cloud-based WMS handle data security?
Leading cloud WMS providers implement multi-layered security exceeding what most companies could deploy independently. This includes physical datacenter security, enterprise-grade firewalls, intrusion detection, and DDoS protection. Data encryption protects information both in transit and at rest. Multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and compliance certifications like SOC 2 and ISO 27001 ensure ongoing protection. Dedicated security teams monitor for threats continuously.




